[OS] Chapter 12 — Mass Storage System
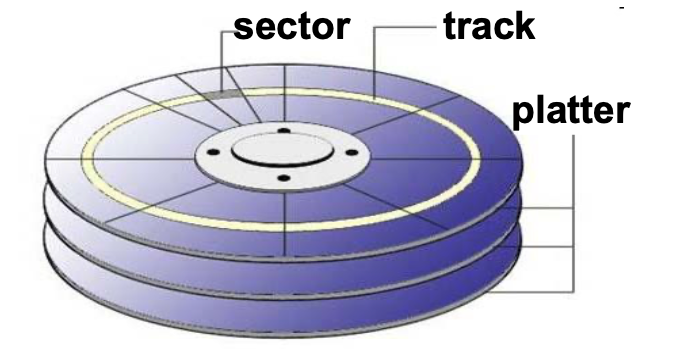
Disk Structure
由磁盤組成,最小儲存單位是 sector,買來就切死的,所以用軟體的 block (多個 sector)來控制。Sector 會有 number,所以可以對特定資料作讀取。
Sectors per Track
- Constant linear velocity ****(CLV)
Density of bits per track 是固定的
這樣內圈的資料量就會小於外圈的
但是這樣讀取資料的速度會不固定
→ 讀內圈要轉比較快
applications: CD-ROM and DVD-ROM
- Constant angular velocity ****(CAV)
- keep same rotation speed
- 內圈 density 比較高
- 這樣轉速就不用改
- applications: hard disks
Disk IO
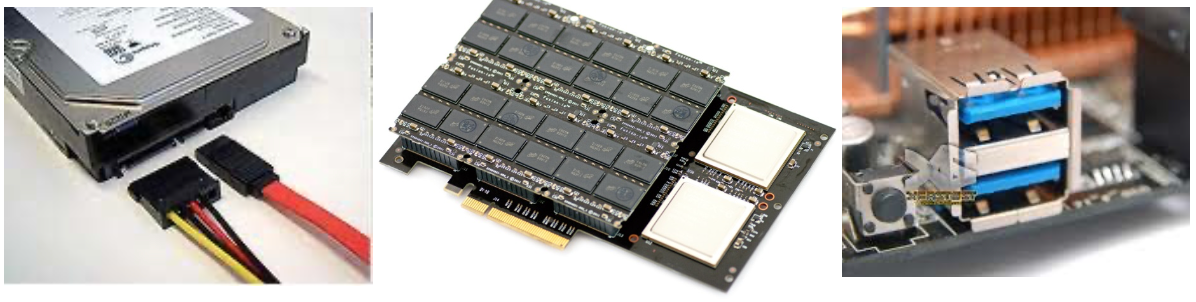
- EIDE, ATA, SATA (Serial ATA), USB, SCSI, etc
- 效能會有差
- I/O bus is controlled by controller
Disk Scheduling
Disk-access time has 3 major components
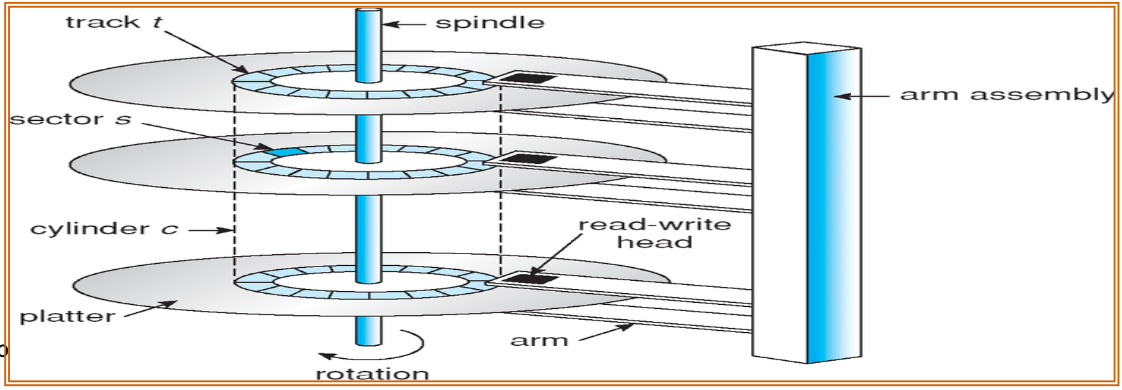
seek time:去移動讀寫頭的位置花的時間(通常最慢)
→ 主要優化目標
rotational latency:轉動磁盤的時間(快到可以被 ignore)
read time:content transfer time(取決於一次讀寫的資料量,也可能這邊最慢)
Disk bandwidth — # of bytes transferred/(complete of last req – start of first req)
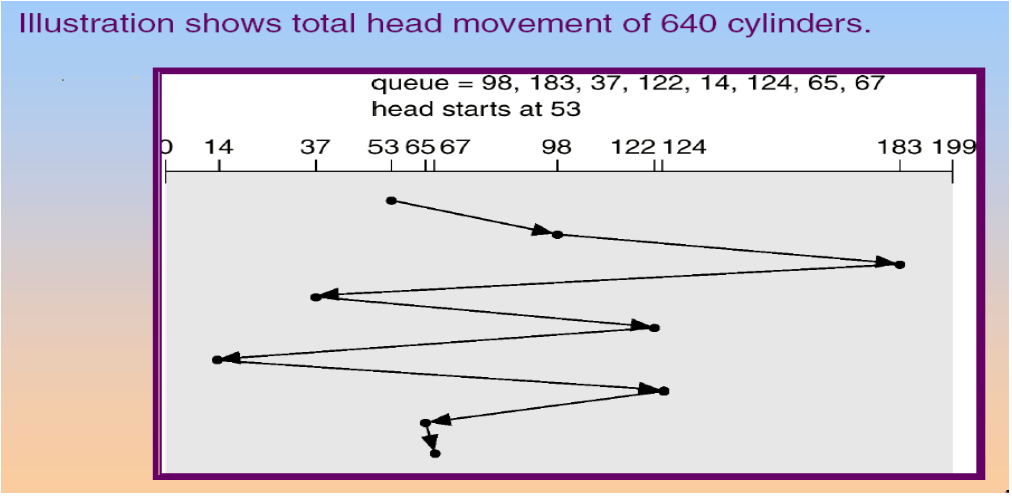
FCFS (First-Come-First-Served)
- 問題的描述方式會是一串數字,代表著他是第幾圈的資料。
SSTF (Shortest-Seek-Time-First)
- 看哪一個離目前的磁頭最近的就去那個(Greedy)
- 有 starvation,因為 request 會不停地發生,所以很遠的可能一直被插隊
- 不是 Optimal,因為只能找現在離我最近的,可能等一下進來的會更近,但是他就跳走了,他應該要停一下等那個未來的傢伙。
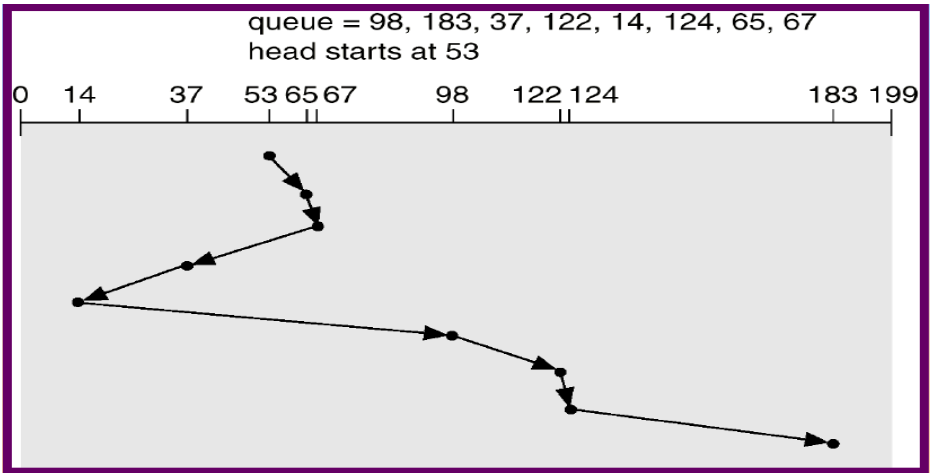
SCAN Scheduling
通常的解
我就移動我的,有剛好可以做的我就做
disk head move from one end to the other end
轉到底會換方向
⇒ 檢查時間不 uniform
A.k.a elevator algorithm
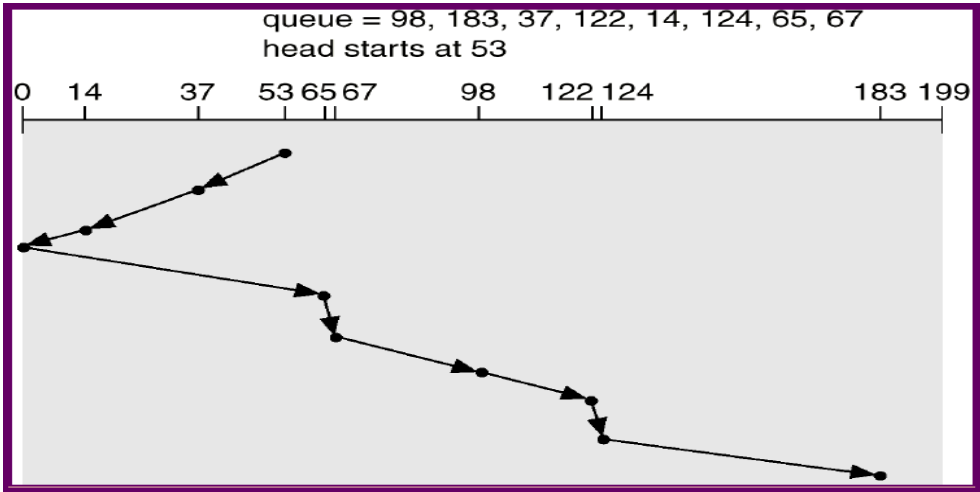
C-SCAN Scheduling
只轉一個方向,走到底就把磁頭拉回去另一端
⇒ 比較 Uniform
(Round robin)
基本上都用這個,不會用 SCAN
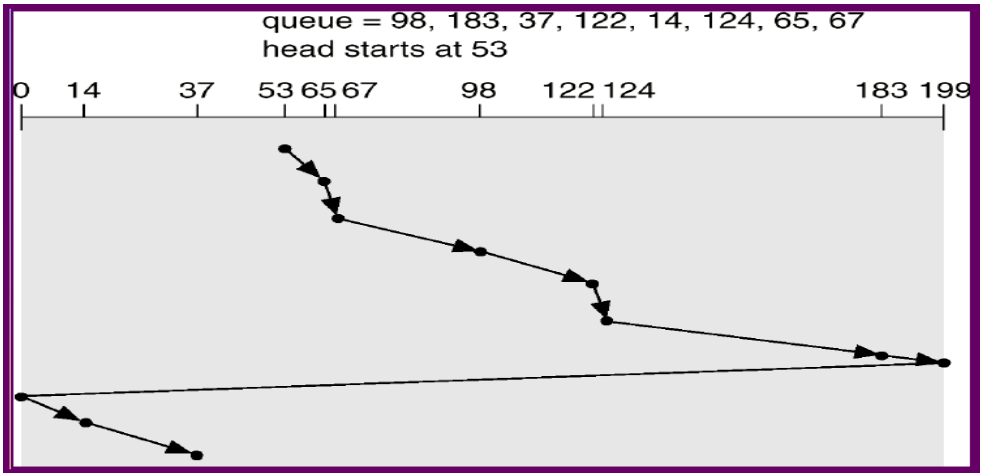
C-LOOK Scheduling
- 一樣只轉一個方向,但是不會走到底
- 如果往右邊走,就會去看右邊的下一個是誰
- 其實跟 SSTF 很像,因為他在也會被剛進來的帶著走(但是不會 starvation)
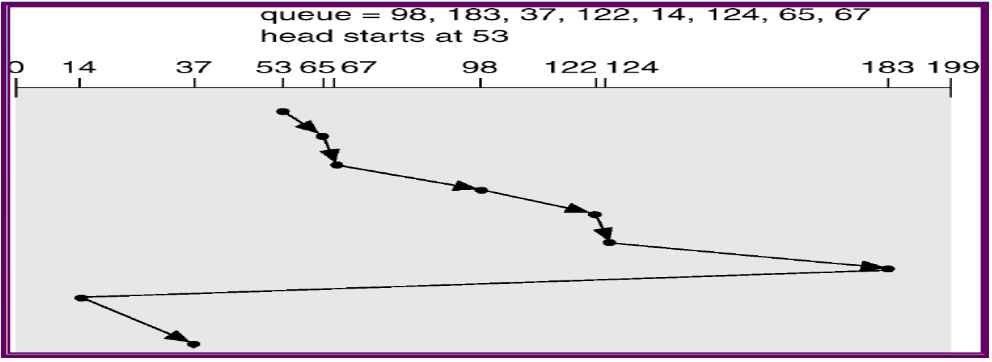
Summary
- SSTF
- common and has a natural appeal, but not optimal
- SCAN
- perform better for disks with heavy load
- No starvation problem
- C-SCAN
- More uniform wait time
- Performance is also influenced by the file-allocation method
Contiguous: less head movement
→ 可能會因為有同時很多 process 在讀,所以還是不 contiguous 的
Indexed & linked: greater head movement
Review Slides (I)
- 3 major components in disk-access time
- Seek
- Rotation
- Read
- Goal of disk-scheduling algorithm
- Disk-scheduling algorithms
- FCFS
- SSTF
- SCAN
- C-SCAN
- C-LOOK
Disk & Swap-Space Management
Disk Formatting
一般的格式化是 high level 的格式化,low level 的 disk 的 formatting(這是出廠前就做好的)是 dividing a disk (magnetic recording material) into sectors that disk controller can read and write 。
- each sector = header + data area + trailer
- Header — metadata,i.e. where the sector is, the ID of the sector
- trailer — error correction code, based on all bytes in data area
- High-level: partition and 用 data block 的方式去存取
Booting
Bootstrap program
Initialize CPU, registers, device controllers, memory, and then starts OS
First bootstrap code stored in ROM
Complete bootstrap in the boot block the boot disk (aka system disk)
Booting from a Disk in Windows 2000
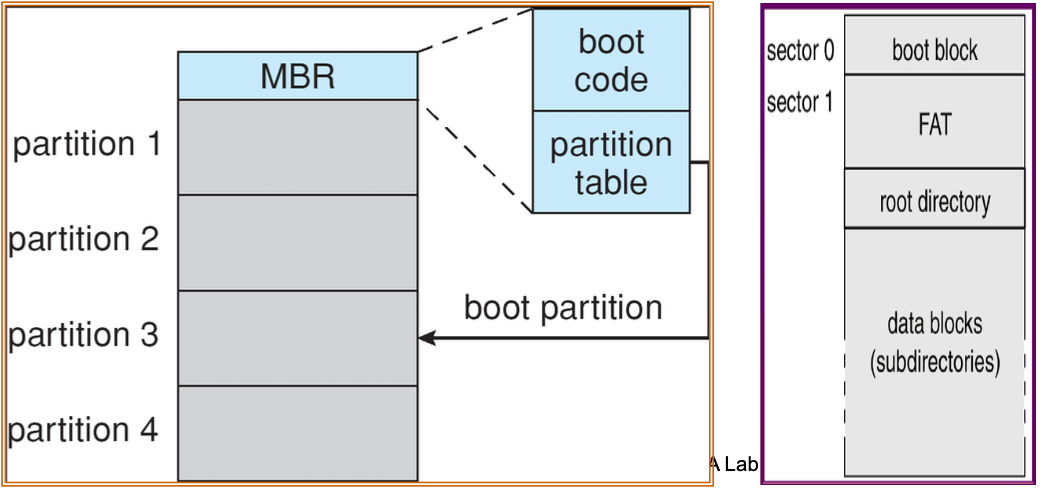
- Run bootstrap code in ROM
- Read boot code in MBR(Master boot record)
- Find boot partition from partition table
- Read boot sector/block and continue booting
Bad block
A.k.a 壞軌
- Disk controller 是第一個去處理的
- IDE — 看 ECC 知道他壞掉就不會讀給上面的,而是 notify 他們說「欸,壞去啊!」
- SCSI — 除了不會讓你用以外,還會把壞掉的地方的儲存空間 recreate
出來,有下面兩種方式
Sector sparing (forwarding) — 像是有空白的撲克牌,有牌不見就拿空的補充。但是這樣連續的 sector # 會存在不連續的地方,所以壞太多效能就會變差。
→ Run time 在用的
Sector slipping — 從壞掉的地方開始全部往後移一格。超花時間。
→ Reboot 在做的
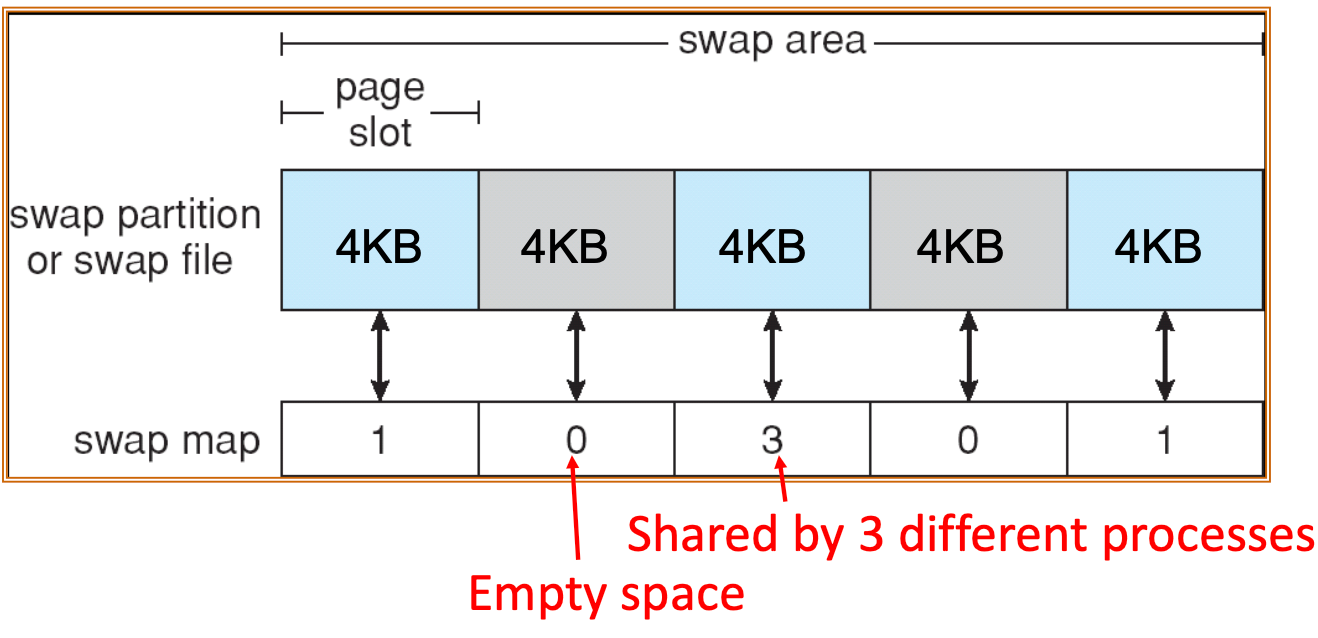
Swap space
- See this
- 之前是說由 Virtual Memory 或是 Memory Manager 。把他切成固定的 page,然後直接 map。
- 他也可以用 File system 來管。把每一個 page 設成 4kb 的 file。當要存取的時候就用 file name 當作 page ID。
- 通常是直接用 Memory Manager 來操作,不通過 file system,比較快。
- 所以用 raw partition 一定比較快,但是這樣就會浪費 raw partition 的空間。且如果 VM 用得很兇,那 swap space 會不夠,那就效能大量下降。
- 所以通常都一起用。
- Swap Space Allocation
- 1st version: disk 和 memory 都一份一樣的
- 2nd version:
- Solaris 1:
- Run time 產生的才存,像是 code 就不用存,反正需要再去 disk 拿就好
- 如果 declare 了但是還沒用,那就不用存在 swap space
- Solaris 2:
- 先不要再 swap space 存 copy,只有在 swap out 才 create
- Solaris 1:
RAID Structure
現在儲存空間越來越便宜。
RAID = Redundant Arrays of Inexpensive Disks
→ 想要用很多便宜的硬碟,產生一個 powerful 的 storage device
→ provide reliability via redundancy (多 backup)
→ improve performance via parallelism (平行化,一起讀寫)
- RAID is arranged into different levels
- Striping → 資料分散
- Mirror (Replication) → 資料 copy
- Error-correcting code (ECC) & Parity bit
RAID 0
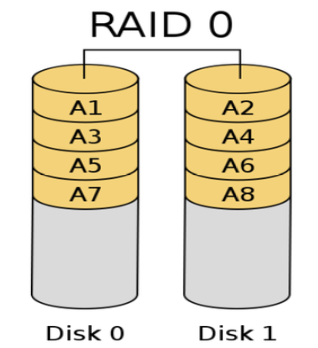
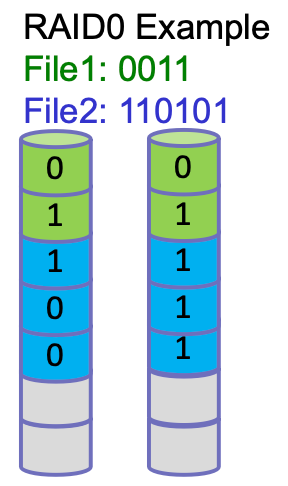
- Striping → 把檔案切割用 Round Robin 的方式擺到印碟上去
- Improve performance via parallelism → 大資料可以同時讀取
RAID 1
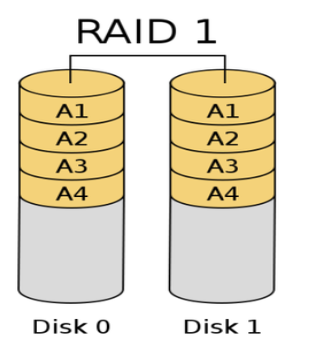
- Mirror → 複製
- Provide reliability via redundancy
→ 通常最多作三個 replica
- 讀取速度會變成 N 倍
- 寫入速度不變
RAID 2: Hamming code
Hamming code → 可以推出是誰遺失然後重建出來
E.g.: Hamming code(7,4)
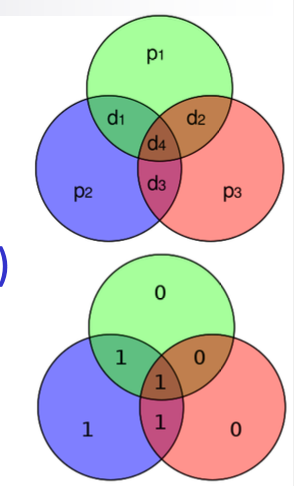
- 4 data bits (on 4 disks) + 3 parity bits (on 3 disks)
- 只浪費的 75%(RAID 1 是 100%)
RAID 3 & 4: Parity Bit
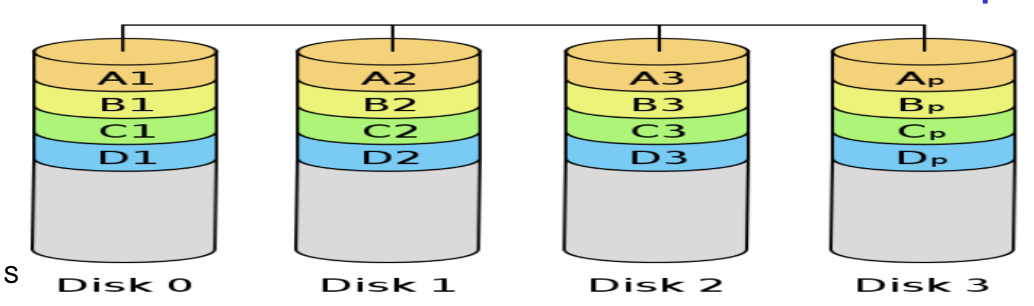
硬碟壞掉,他本來就會自己說,所以應該是不用偵測的,我們只需要 recovery
→ a single parity bit is enough to correct error from a single disk failure
→ 所以我們只需要浪費
1/NRAID3: Bit-level striping; RAID 4: Block-level striping
→ RAID 4 recover 的速度會略快(除非壞掉的只有一個 bit),因為讀取都是一個 block 在操作的,所以他就不用橫跨好幾的 disk 了
讀取速度是
N - 1倍,寫入速度不變(因為要去寫存 Parity bit 的那顆)
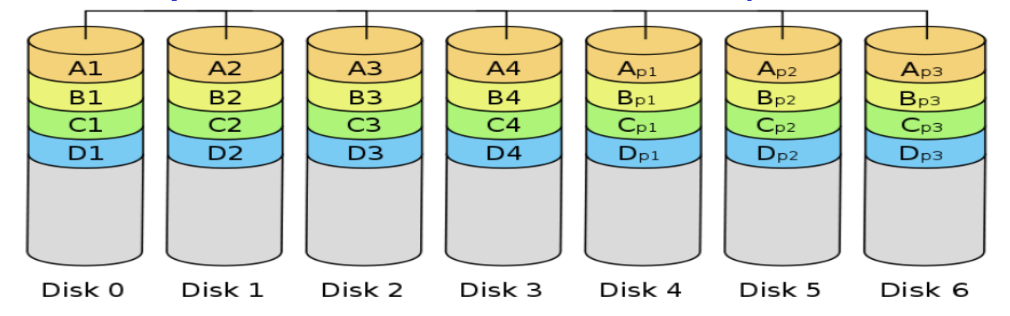
RAID 5: Distributed Parity
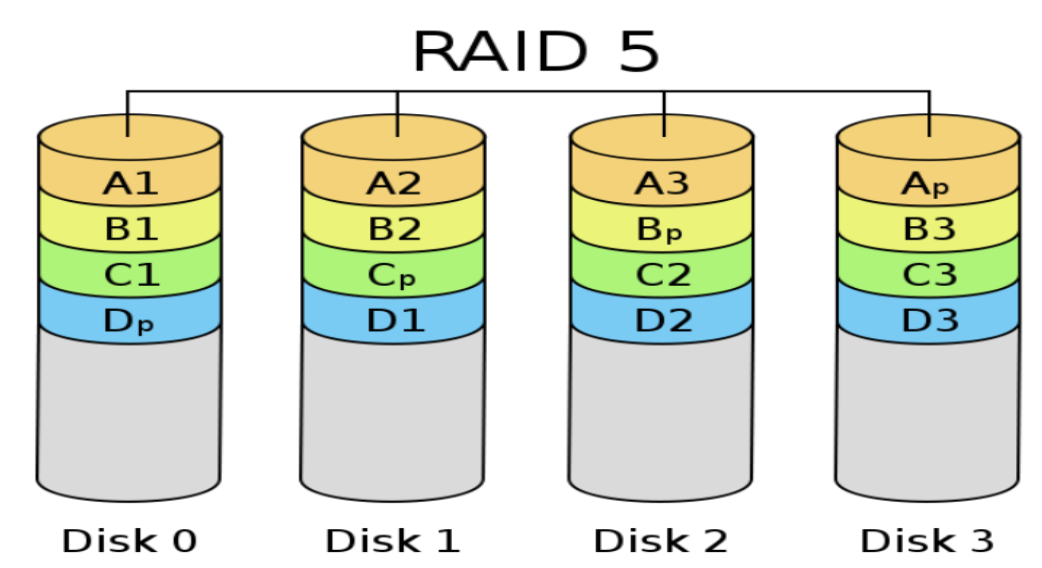
- Load balancing → 把 parity bit 分散在各個 disk
- 最常見的
- Read 可以是
N倍了 - Write
Method 1
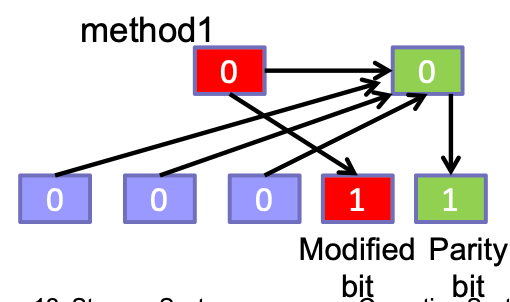
- 讀 N-2 筆 data
- 重算 pb
- 寫進去那兩個
⇒ N / (N - 2 + 2) = 1
Method 2
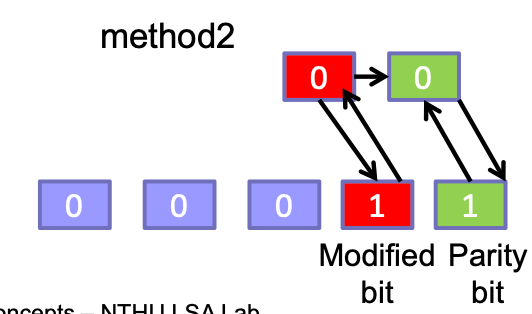
- 讀原本的值
- 算出修改的影響
- 寫入
⇒ N / 4 times faster
RAID 6: P+Q Dual Parity Redundancy
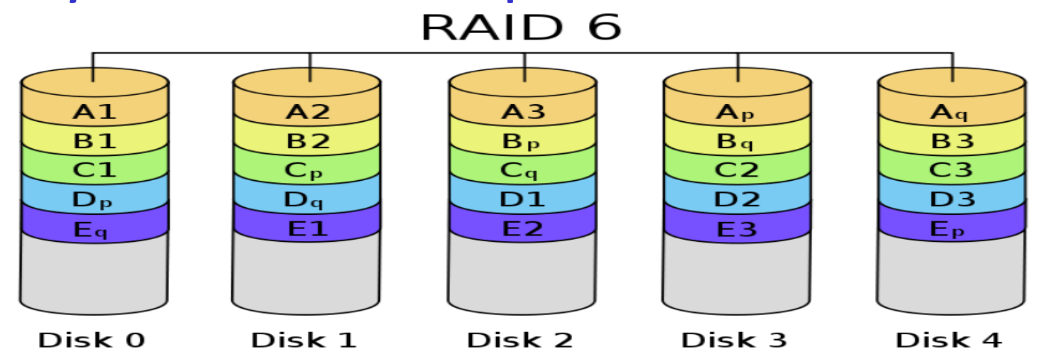
- 你有不只一個 PB ⇒ 可以多個硬碟壞掉
Hybrid RAID
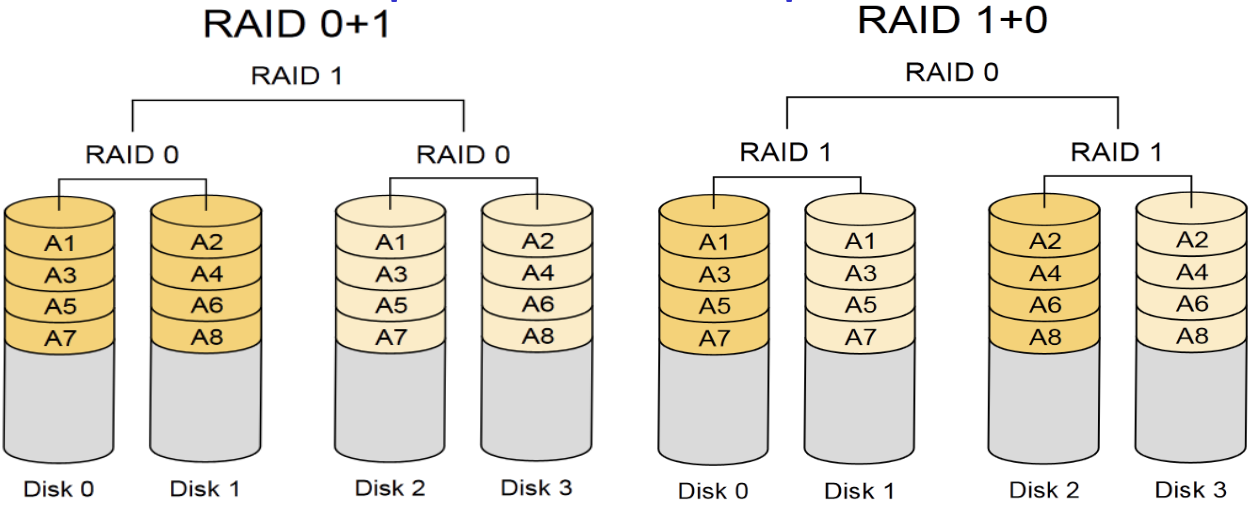
- RAID 0+1: Stripe then replicate → 保護能力比較弱
- RAID 1+0: Replicate then stripe
- 先寫先做
Review Slides (II)
- Swap space using FS? Raw partition?
- How to reduce swap space usage?
- RAID disks? Purpose?
- RAID-0~6?
- RAID 0+1, RAID 1+0
Textbook Questions

此筆記為清華大學周志遠教授作業系統之課堂筆記,所有內容及圖片皆取材於課堂內容。
如內容有誤,歡迎來信 mail@arui.dev。